
MR imaging with intravenous contrast enhancement has been shown to identify thickened synovium in RA 4 6–8 and may permit the precise identification of equivocal or unsuspected synovial disease processes. 3, 4 Heavily T2 weighted images may allow such a discrimination 5 however, signal contrast between the two tissues may be insufficient to allow image analysis techniques to separate the synovial lining from synovial fluid. For example, there may be difficulty discriminating between the synovial lining and synovial fluid with conventional T1 and T2 weighted sequences in the knees of RA patients. 2 However, clinical assessment of synovial swelling is qualitative and quantification of synovial lining volume by imaging techniques may provide a more reliable index of synovial disease and, therefore, be of greater assistance in the management of chronic synovitis.Īlthough magnetic resonance (MR) imaging has been shown to be useful in the assessment of joint abnormality in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 3 there is no consensus over the optimum MR methods for imaging synovial tissue in disease. 1 Clinical assessment of synovial swelling taken together with pain, tenderness, and stiffness, remains the most direct indicator of current disease activity in a given joint and is of particular importance when evaluating the response to local treatment, such as intra-articular glucocorticoid injection.
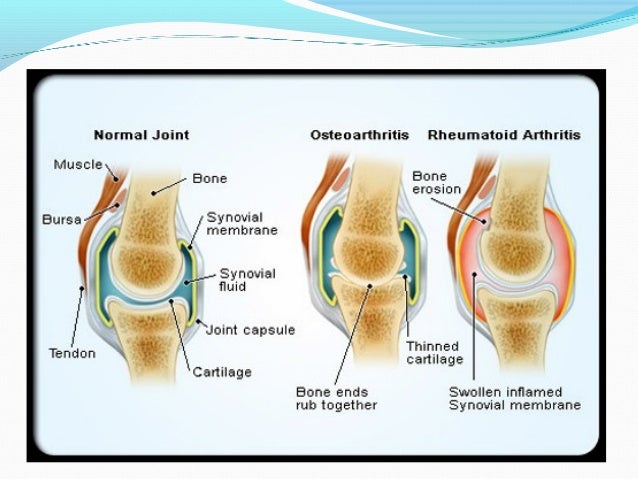
In chronic synovial inflammation, the synovial lining becomes swollen mainly as a consequence of an increase in tissue cellularity and fibrosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
